Heartburn
Struggling with heartburn? Here’s what you need to know to find relief.
ALL TEST ARE ACCREDITED & REGULATED BY



What is heartburn?
Heartburn is a burning pain in your chest. This pain is caused by stomach acid rising from your stomach into your oesophagus (the pipe that takes food from your mouth to your stomach).
This can cause:
- Burning pain in the middle of your chest
- Pain which is worse when you bend over or lie down
- Burning pain that radiates into your back
By learning more about the causes of, tests for, and treatment for heartburn, you can understand it better and make informed decisions to get back on track.

Why does heartburn happen?
There are several possible causes of heartburn, and it’s important to find out what’s causing yours.
Here are the main causes of heartburn:
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GORD)
Hiatus hernia, when part of your stomach moves up into your chest
Surgery you’ve had in the past (especially bariatric surgery)
Certain foods and drinks, such as alcohol, coffee, chocolate, and fatty or spicy foods
Being overweight
Smoking
Pregnancy
Stress or anxiety
Medication, such as anti-inflammatory painkillers
Overgrowth of bacteria in your small intestine (this is called SIBO)


Diagnosing heartburn
Diagnostic testing allows us to pinpoint the exact cause so we can recommend the right solution.
Oesophageal manometry, 24-hour pH, malabsorption breath tests, SIBO & gastric emptying
At the Functional Gut Clinic, we use the following highly accurate and trusted diagnostic tools, to identify the underlying cause of your heartburn:
Oesophageal manometry – which measures the function of your oesophagus (food pipe)
24-hour pH impedance monitoring – which looks at whether you have any reflux
Carbohydrate malabsorption breath test – which finds out if you have certain food intolerances (lactose or fructose)
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) breath test – which finds out if you have an overgrowth of bacteria in your small intestine (called SIBO)
Gastric emptying test – which measures how quickly food leaves your stomach
Learn more about heartburn

Heartburn During Pregnancy and How to Deal with It
Expectant mothers often complain of heartburn as their pregnancy progresses. In fact, it affects more than half of pregnant women in their second and third trimesters.
Heartburn, often associated with acid reflux, occurs when acid from the stomach moves backwards into the esophagus, causing irritation and inflammation. In severe cases, the acid can even reach the throat and mouth, leading to symptoms like hoarse voice, bad taste, and tooth decay.
But why does this occur? And what can expectant mothers do about it? Here’s how to deal with heartburn during pregnancy:
Heartburn During Pregnancy
Heartburn is a “burning sensation” behind the breastbone that occurs when stomach acid flows from your stomach into the food pipe (oesophagus). Usually, the condition is mild and is linked to something you eat.
However, in pregnant women – especially during the final stages – heartburn can become severe and persistent. It’s estimated that 30-80% of pregnant women experience heartburn.
Heartburn Symptoms
Unsure if you’re experiencing heartburn? Look for these symptoms:
Burning sensation in the chest or throat
Chest pain
Sour or bitter taste in the mouth
Regurgitation of food or acid
Bloating
Feeling of fullness after eating small amounts
Frequent burping
Worsening of symptoms when lying down or after meals
What Causes Heartburn During Pregnancy?
Heartburn is a typical symptom of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GORD). This condition occurs when the stomach contents repeatedly backflow into the oesophagus over a long period of time.
In pregnant women, the increased risk of GERD is related to their body changes. Three common causes include:
Hormones. Progesterone (the “pregnancy hormone”) is a well-known muscle relaxer. It can relax the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) that usually separates the stomach from the esophagus, allowing for backflow.
Growing Baby. As the baby grows, it increases the pressure in the abdomen. This rising pressure pushes the stomach contents backwards.
Slowed Digestion. Progesterone also slows the movement of food through the digestive system. As a result, the stomach remains fuller for longer, increasing the risk of heartburn.
How to Deal with Heartburn During Pregnancy
Heartburn often becomes more common later in pregnancy. But it’s not inevitable. With a few sensible lifestyle changes and treatments, you can reduce your symptoms.
(Note: It's also important to distinguish heartburn from other conditions that might involve regurgitation, such as rumination, where food is re-chewed and re-swallowed, or sometimes expelled.)
Here’s how:
Change Your Diet
Your diet can significantly increase the risk of heartburn. For example, many people find that spicy, acidic, or high-fat foods trigger their symptoms.
Avoiding these foods might help:
Spicy foods
Fried or fatty foods
Citrus fruits (e.g. oranges, lemons)
Tomatoes and tomato-based sauces
Chocolate
Caffeinated drinks (e.g. coffee, cola)
Carbonated drinks
Peppermint
Onions and garlic
Eat Little and Often
We’re used to eating three main meals per day. However, as the body grows, your stomach can no longer handle that volume as well.
Instead, try eating smaller meals and spread more frequently throughout the day. This allows the stomach to empty quicker and avoid overwhelming it.
Don’t Lie Down Right After Eating
Gravity is your friend. Once you’ve finished eating, stay as upright as possible for the next three hours. This gives your stomach time to empty and relax. It minimizes the risk of backflow from your stomach into your oesophagus.
You should also avoid eating just before bed. Follow the same three-hour window, letting your stomach empty before you lie down for the night.
Prop Up Your Head When You Sleep
If you experience repeated acid reflux during the night, it’s likely because you’re lying flat. Try adding an extra pillow under your head and shoulders (or even raise your bed using blocks). This will let gravity work its magic and prevent acid from flowing backwards.
It’s sensible to raise your head up around 6 to 9 inches, allowing gravity to do the work for you.
Drink After Meals
Drinking with meals increases the risk that your stomach becomes too full.
Instead, try to drink after your meal. This gives your stomach a chance to digest and process the food before filling up its capacity.
Take Medication
If none of the lifestyle and dietary approaches above do the trick, you might want to consider taking a medication to prevent the reflux.
Antacids are the most common way to treat an acid attack. These tablets neutralize the acid in your stomach, preventing heartburn. But you should only take antacids that contain calcium carbonate. Avoid antacids containing sodium bicarbonate as this can increase swelling.
Other medications to treat heartburn aren’t advised during pregnancy and taking them can potentially cause harm to the developing baby.
Ready to Find Relief from Heartburn During Pregnancy?
If morning sickness or that burning chest feeling is making pregnancy less comfortable, don’t suffer in silence. At The Functional Gut Clinic, our friendly specialists offer tailored advice and expert care to help manage heartburn throughout your pregnancy journey.
Find out more about heartburn symptoms and how we can diagnose the underlying cause.
Heartburn is a burning pain in your chest.
Heartburn is often experienced after eating and can last anywhere from a few minutes to several hours. The stomach releases more acid after eating certain foods, including spicy dishes, fatty foods, citrus fruits, tomato-based products, garlic, and caffeinated drinks. The more acid that is produced, the greater the risk of heartburn.
Other factors include obesity, smoking, stress, pregnancy, and eating too close to bedtime.


What are the symptoms of heartburn?
Heartburn primarily causes an uncomfortable or burning sensation in the middle of your chest. You may also experience:
A burning sensation in your throat
A strong acidic or sour taste in your mouth
Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
A feeling of pressure or pain behind your breastbone
Repeated coughing
Hoarse voice
In addition to these symptoms, the pain from the acid can get worse when lying down or bending over. This is because the acid flows out of the stomach and into the oesophagus. Whenever you lie down, you increase the risk of heartburn-related symptoms.
Constant heartburn is a sign of a severe underlying condition. Most people experience heartburn in episodic attacks – usually after consuming certain foods. If the heartburn is persistent, it’s crucial to speak to a medical professional. You can also consider organising a test via The Functional Gut Clinic (see below).
What causes heartburn?
Heartburn occurs when the contents of the stomach enter the oesophagus (the food pipe connecting your stomach to your throat). Usually, the stomach contents are prevented from going back into the oesophagus by a juncture called the lower oesophageal sphincter. However, in some people, this sphincter doesn’t function properly.
Heartburn is a symptom of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GORD). GORD simply refers to the backflow of acid from the stomach into the oesophagus. GORD is the condition; heartburn is the symptom.

Several factors increase the risk of heartburn. The causes of heartburn and GORD either increase acid production within the stomach or affect the functioning of the lower oesophageal sphincter. These include:
Hiatal hernia. A hiatus hernia involves a part of your upper stomach penetrating through the diaphragm (the layer of muscle separating your chest from your stomach). This usually occurs due to a weakness or tear.
Pregnancy. If you become pregnant, the increased pressure during the third trimester (and sometimes earlier) forces the stomach contents backwards, causing heartburn.
Surgery. Previous surgery, especially bariatric surgery, increases the risk of not only heartburn but also a hiatus hernia.
Smoking. Smoking is closely linked to heartburn and GORD. People who quit smoking notice a significant reduction in heartburn symptoms.

Overweight or obesity. Being overweight or obese is a major risk factor for GORD. This is likely due to the increased pressure in the stomach alongside a diet high in fatty, processed foods.
Medications. Certain medications, such as anti-inflammatory painkillers (e.g., ibuprofen or aspirin), sedatives, and blood pressure medications, can increase your risk of heartburn.
Stress or anxiety. An increase in stress or anxiety can increase acid production in some people, leading to heartburn. It’s often accompanied by another factor.
Small intestine bacterial overgrowth (SIBO). Excessive bacterial growth in the small intestine leads to increased abdominal pressure and subsequent acid reflux, which can cause heartburn. Managing SIBO often reduces these symptoms.
Foods to avoid
Acid production is a normal part of the stomach’s function. The acid helps digest food. Certain foods require more acid to digest, triggering an increased production in the stomach.
For most people, this isn’t an issue as the acid flows into the small intestine. However, if you struggle with heartburn and GORD, then it’s sensible to limit or avoid certain foods. These include:
Citrus fruits (like oranges and grapefruits)
Tomatoes and tomato-based products
Spicy foods
Garlic and onions
Chocolate
Mint
Fatty or fried foods
Caffeinated beverages (such as coffee and tea)
Carbonated drinks
Alcohol
It’s not just the food. Eating an excessively large meal, wearing tight clothes, and lying down soon after eating can increase the risk of heartburn. If you’re experiencing persistent heartburn, it’s often linked to diet rather than another factor.

Is heartburn the same as GORD?
No. Heartburn specifically refers to the burning sensation in the chest. GORD is the underlying condition involving the backflow of acid. Heartburn is a symptom of GORD. Acid reflux is sometimes used as shorthand for GORD – however, not every attack of acid reflux is an example of GORD.
Acid reflux refers to any episode of acid backflowing into the oesophagus. If the episodes occur two or more times a week, it is diagnostic for GORD. Most people experience acid reflux episodes occasionally. This can increase in frequency as acid reflux progresses to GORD. You should speak to a doctor if you notice this change.

Does acid reflux always cause heartburn?
Heartburn is always caused by the backflow of acid into the oesophagus. Several other conditions can create a similar sensation. For example:
Oesophageal ulcers. Ulcers occur due to erosion of the oesophageal lining. Often associated with acid reflux or overusing anti-inflammatory medications.
Oesophagitis. Severe inflammation of the oesophagus is closely linked to GORD. However, it can also be caused by medications and infections. An allergic condition known as eosinophilic oesophagitis can also cause heartburn.
Functional heartburn. Unlike the other conditions, this isn’t a problem with your oesophagus or stomach. It’s caused by a disorder of the gut-brain connection. It involves the same heartburn symptoms but without any signs of acid reflux or inflammation. It’s connected to overactive nerves.

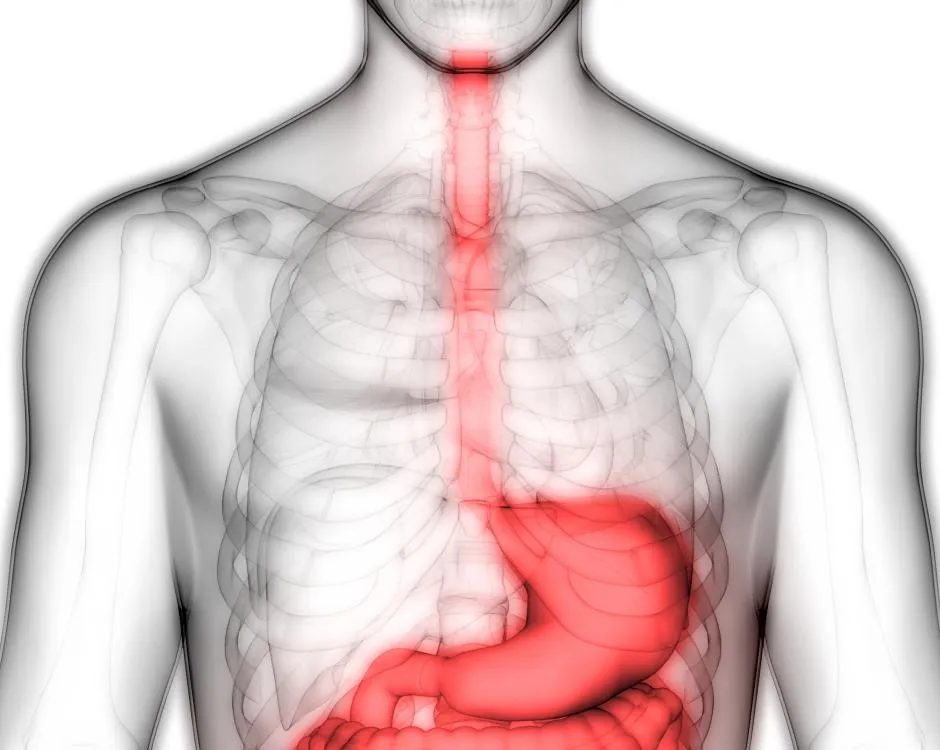
How long does heartburn last?
Heartburn is not a permanent condition. It lasts as long as the acid is present to irritate the oesophagus and throat. Most people experience heartburn and GORD for between a few minutes to several hours. The timespan often depends on the underlying cause. For example, if your heartburn is due to your diet, it might go away within a few minutes. In contrast, if you have a hiatus hernia, the heartburn might persist for much longer, even after standing up.
Constant heartburn is a rare symptom. It’s a concerning sign, as the acid can continue to damage your oesophagus. If you’re constantly feeling heartburn (or using lots of antacids), then it’s critical to speak to a doctor.
Is heartburn serious?
Most cases of heartburn aren’t serious. It’s common to experience heartburn after a large meal or eating certain foods. However, if the heartburn becomes repeated or constant, it can cause long-term damage. Usually, the damage caused by acid reflux heals like any injury. If it happens regularly, then the oesophagus lining can become permanently injured.
Potential long-term complications include:
Oesophageal strictures. The lining of the oesophagus becomes replaced with scar tissue due to repeated inflammation. This scar tissue causes a narrowing of the oesophagus (stricture), which prevents food from getting through.
Intestinal metaplasia. The tissue lining of the oesophagus undergoes a change to look more like the lining of your intestines, protecting it from damage. It is called Barrett’s oesophagus and is a precancerous condition.
Oesophageal cancer. Cancer is a rare complication of GORD and heartburn. It occurs due to persistent inflammation and cellular changes. The longer your heartburn persists, the greater the risk of cancer.
Heartburn and GORD can also indicate problems in your stomach. For example, excess acid production can lead to gastritis (stomach inflammation) and stomach ulcers. It may also aggravate preexisting conditions such as asthma.
How do we diagnose the causes of heartburn?
The following tests may be used to diagnose what is causing your heartburn:
Oesophageal manometry – which measures the function of your oesophagus (food pipe)
24-hour pH impedance monitoring – which looks at whether you have any reflux
Carbohydrate malabsorption breath test – which finds out if you have certain food intolerances (lactose or fructose)
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) breath test – which finds out if you have an overgrowth of bacteria in your small intestine (called SIBO)
Gastric emptying test – which measures how quickly food leaves your stomach
The following tests may be used to diagnose what is causing your heartburn:
Oesophageal manometry – which measures the function of your oesophagus (food pipe)
24-hour pH impedance monitoring – which looks at whether you have any reflux
Carbohydrate malabsorption breath test – which finds out if you have certain food intolerances (lactose or fructose)
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) breath test – which finds out if you have an overgrowth of bacteria in your small intestine (called SIBO)
Gastric emptying test – which measures how quickly food leaves your stomach

Heartburn treatment
Lifestyle changes
Most people who experience occasional heartburn symptoms can benefit from lifestyle changes. This involves limiting exposure to potential triggers. You might want to try:
Avoiding trigger foods, such as fatty foods or caffeinated beverages
Eating smaller meals
Avoiding tight clothing
Avoiding lying down immediately after eating
Quitting smoking and alcohol consumption.
Often, people find that small changes to their diet can stop or reduce episodes of heartburn. If the heartburn continues, it’s usually a sign that something else is going on. It’s crucial to get to the bottom of your symptoms; otherwise, they will persist.

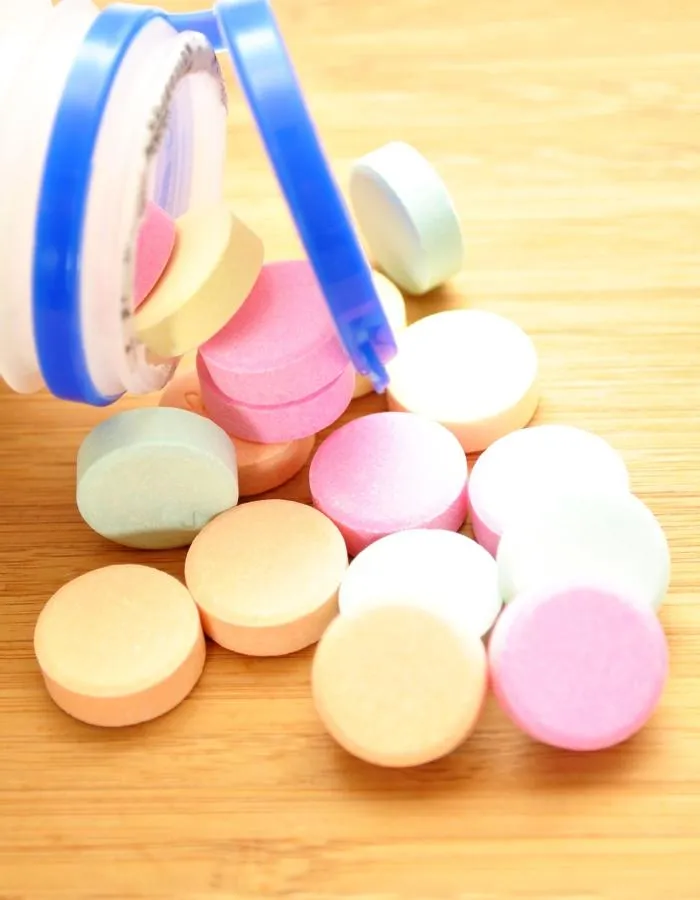

Medication
As heartburn is caused by acid, neutralising this acid relieves symptoms. The primary treatment for heartburn is an over-the-counter (OTC) antacid, such as Gaviscon or Alka-Seltzer. These medications provide immediate relief from your symptoms – perfect for tackling a sudden acid reflux attack. If you experience constant heartburn, it’s sensible to carry antacids with you. However, excessive use of antacids can cause other problems.
Your doctor may prescribe medications that prevent acid production. This includes:
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs). These medications reduce stomach acid production by blocking the enzyme in the stomach lining that produces acid. Common examples include omeprazole, esomeprazole, and pantoprazole. PPIs are used to treat GORD by allowing the oesophagus to heal and preventing further damage.
H2 Receptor Antagonists. These drugs work by blocking H2 receptors on stomach cells that signal the production of acid. This results in decreased stomach acid output. Examples include ranitidine, famotidine, and cimetidine. They are effective in relieving GORD symptoms and are generally used for milder cases.
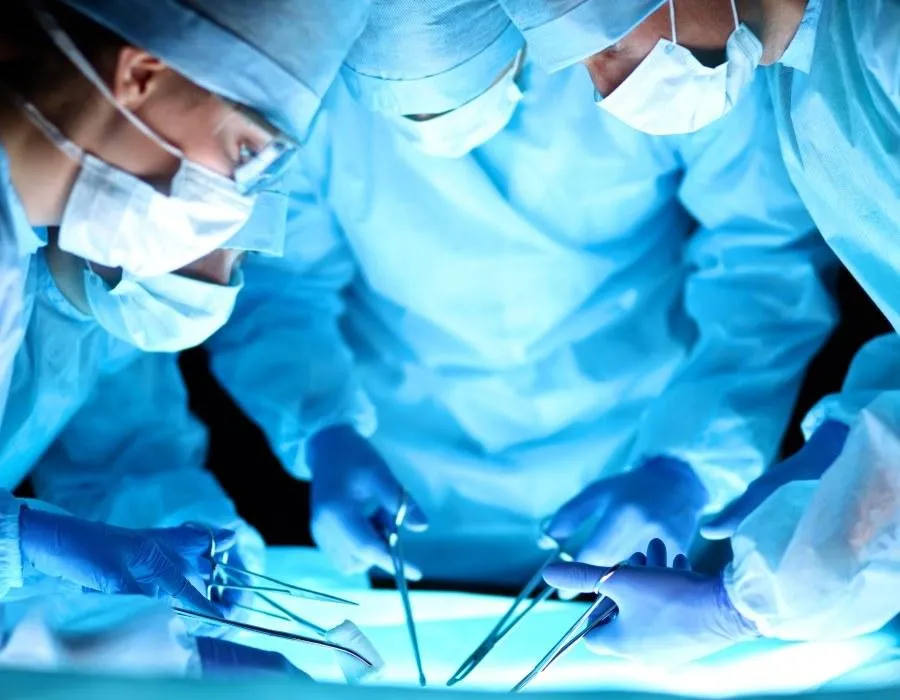
Surgery
In the majority of cases, lifestyle changes and medication are enough to prevent heartburn symptoms. If GORD doesn’t respond to medication, surgery might be a potential option. This can repair a hiatus hernia, strengthening the lower oesophageal sphincter and permanently preventing the backflow of acid.
Procedures include:
Nissen fundoplication. This procedure tightens the junction between the stomach and the oesophagus.
Transoral incisionless fundoplication. A similar procedure performed non-surgically using an endoscope.
LINX device. A tiny ring of magnets is placed around the junction between the stomach and oesophagus to prevent reflux. It’s a type of minimally invasive surgery.
When should you seek medical care for heartburn?
Heartburn is extremely uncomfortable. However, most cases are relatively mild and treatable with antacids. Speak to a medical professional if:
You experience heartburn more than once a week
You have other associated symptoms
You have difficulty swallowing
Your heartburn persists despite treatment
You’re over the age of 60
You have a tight or squeezing chest pain
You cough up blood
Remember, occasional heartburn is relatively normal. But if you have constant heartburn, it’s crucial to get tested. The Functional Gut Clinic is highly experienced in diagnosing acid reflux. We’ll organise your test and provide advice on what to do next.

Hear from people we’ve helped, just like you.
"Very professional while welcoming and friendly"
"The manner and demeanour of all staff from reception to people carrying out the test was very professional but welcoming and friendly. Atmosphere is very relaxed and all instructions clear and concise."
London Patient

"Highly recommend this"
"Thanks to Dr Hobson and everyone at the Functional Gut Clinic. The whole team is very kind and generous and they are doing things that are cutting edge and they actually get results."
Manchester Patient

"Highly recommend this"
"After stopping my lansoprazole, every time I had a warm drink, I could feel it burn all the way down to my stomach. Thank you to Sam for making me feel at ease." - Manchester Patient

"My experience could not be better"
"Pleasant and knowledgeable staff that made the experience more enjoyable than it should be!" - London Patient

"Very friendly and knowledgeable"
"An excellent service from beginning to end. I would recommend to anyone who was considering having testing done. Very friendly and knowledgeable!" - Manchester Patient

"Very kind and helpful"
"It was also great to have time to talk to the clinicians – very important when you have problems. Reception staff also very kind and helpful." - Manchester Patient

Are you experiencing any other symptoms
Symptoms are often closely connected. Find out more below.
Reflux
Burning mid-chest, worse when bending or lying down
Constipation
Difficulty going to the toilet, unusual stools, often with stomach ache or intestinal cramps, bloating, nausea or appetite loss
Bloating

Feeling uncomfortably full and tight, excess belching/breaking wind, abdominal pain or gurgling
Regurgitation

Bringing food or drink back up, difficulty swallowing, feeling that food or drink is stuck in your throat, horrible taste in your mouth
Swallowing Issues
Dysphagia - difficulty swallowing, feeling that food or drink is stuck in your throat, horrible taste in your mouth
Diarrhoea
Loose or explosive stools, can’t get to a toilet in time
Abdominal Pain
Cramps; sharp or dull pain, Bloating, Excessive belching, Nausea or vomiting
Faecal Incontinence

Stools leak unexpectedly, Can’t get to a toilet in time
IBS
Abdominal pain or cramping, bloating, changes in bowel habits and urgency, gas

